When a manga becomes successful, the spotlight usually falls on the mangaka. Meanwhile, in the background are mangaka assistants, who typically remain unnamed and uncredited. But did you know that many famous mangakas started as mangaka assistants?
Mangaka assistants, as the name implies, assist mangakas in the development of manga. Their scope of work includes drawing backgrounds, inking, and pasting screen tones.
Still, this depends on the mangaka they work for and the manga they are creating. Read on if you want to learn more about these nuances and understand what it means to be a manga assistant.
Table of Contents
What Does a Mangaka Assistant Do?
A mangaka assistant does all the background work of the manga, everything except character drawings. Some mangakas even have assistants for every step of the production process.
The most common tasks delegated to mangaka assistants include:
⦁ Creating outlines and layouts
⦁ Lighting and shading
⦁ Drawing backgrounds and crowds
⦁ Pasting screen tones
⦁ Filling in the artwork details
⦁ Framing scenes
⦁ 3D modeling
⦁ Cleaning up the panels
⦁ Serving as a soundboard for ideas
Some assistants are also hired to draw particular things.
Examples:
Go Nagai, mangaka of Mazinger Z, hired assistants to draw military vehicles.
Kaoru Mori, mangaka of Emma, also employed assistants that specialized in photorealistic architecture.
The bulk of the work depends greatly on how their mangakas function. The assistant’s role is also dependent on what their mangakas would assign to them.
Example:
Saito Takao, the mangaka of Golgo 13, only draws the main characters. Everything else is delegated to his assistants.
Meanwhile, Eiichiro Oda, the mangaka for One Piece, likes to handle most of the work. His assistants only draw the background and static objects.
How Much Does a Mangaka Assistant Make?
On average, mangaka assistants are paid 180,000 yen ($1,624.16) per month. They are not entitled to royalties and licensing profits.
However, a mangaka can choose to give them bonuses as he desires. This is because he – not the publication company – shells out the money for them.
Yoshihiro Togashi of Hunter x Hunter paid his assistants a yearly bonus. The bonus equates to four months of their salary at the rime.
Some mangakas have been recorded to pay up to 600,000 yen ($5,415.45) per month. An example of this is Shunsuke Kakuishi, mangaka of Yawara no Michelangelo. He pays his assistants 20,000 yen ($180.52) per day.
But it is important to remember that these variations depend on the mangaka. For the most part, mangaka assistants are considered overworked and underpaid.
How many assistants does a mangaka have?
Mangakas have an average of three assistants. More successful mangakas have around five to seven assistants. A few have more than ten, but that’s considered rare.
Meanwhile, starting mangakas without much money have none or just one.
It boils down to how much work needs to be done, the budget of a mangaka, and how much work the mangaka can take on.
Here is a list of famous mangakas and the average number of assistants they employed:
| Mangaka | Manga | Number of Assistants |
|---|---|---|
| Kentaro Miura | Berserk | 4 |
| Eiichiro Oda | One Piece | 5 |
| Gosho Aoyama | Detective Conan | 6 |
| Akira Toriyama | Dragon Ball | 2 |
| Naoki Urasawa | Monster | 13 |
| Katsuhiro Otomo | Akira | 2 |
| Takehiko Inoue | Slam Dunk | 5 |
| Tite Kubo | Bleach | 3 |
Does a Mangaka Need an Assistant?
A mangaka needs to have at least one assistant. But there are rare mangakas who want to do all the work on their own. This is neither recommended nor humane.
Just look at Eiichiro Oda. He is known in the industry to be highly hands-on with his work. Still, even with five assistants to do the lighter tasks, he only gets three hours of sleep per day. Without assistants, he’ll probably have no rest at all!
This is particularly true for mangakas who are serialized in weekly manga anthologies. They have to produce 20 pages of content every week. That is extremely difficult to do if they don’t have assistants to divide the work with.
This sentiment is echoed by Jamie Lynn Lano, who worked as an assistant to mangaka Takeshi Konomi. In her experience, having more assistants helps the development of the manga. Hence, more successful mangakas hire as many assistants as they need.
However, mangakas who are starting likely have little to no budget to hire assistants. In this scenario, at least ask a friend to help will benefit them greatly.
How are Mangaka Assistants Treated?
Most mangaka assistants are given fair pay.
Mangaka assistants are usually treated well by their respective mangakas. This is especially seen in mangakas who used to be mangaka assistants themselves.
Example:
Shuho Sato, mangaka of Umizaru, used to be an assistant to Nobuyuki Fukimito. He worked around 20 hours a day and only got to sleep for 1-2 hours. His pay was just 200 yen ($1.80) per hour, with no overtime pay.
Because of his experience, Shuho vowed to do better when he became a mangaka himself. Now, he gives his assistants a raise twice per year. They also get a yearly bonus that is equivalent to four months’ pay. He gives them holiday breaks, only asks them to work five days a week, and covers their insurance.
Mangakas and assistants have good camaraderie.
On a more personal level, Jamie Lynn Lano stated that Takeshi Konomi was like her brother. When she wanted to quit because she was burnt out, he was very understanding. He also threw her a grand going-away party.
Although she shared that her pay wasn’t that great, she remembers her experience fondly. Most of that is due to how good the relationships were within their team. It is likely that if a workplace is toxic, assistants won’t want to stay.
Mangakas help their assistants get a head start.
Some mangakas also help their assistants get a start in the industry.
Examples:
Hiroyuki Takei is the mangaka of a widely successful Shaman King. He was an assistant to Nobuhiro Watsuki, mangaka of Rurouni Kenshin. And Nobuhiro himself used to be an assistant to Takeshi Obata, mangaka of Death Note.
Masashi Kishimoto of Naruto also passed the baton to his assistant, Mikio Ikemoto. They worked together for fifteen years on Naruto. After the series finished, Shueisha asked Kishimoto also to create a sequel. Kishimoto then told them to tap Ikemoto, who is now the main mangaka for Boruto.
Here is an elaborate chart showing famous mangakas and successful assistants:
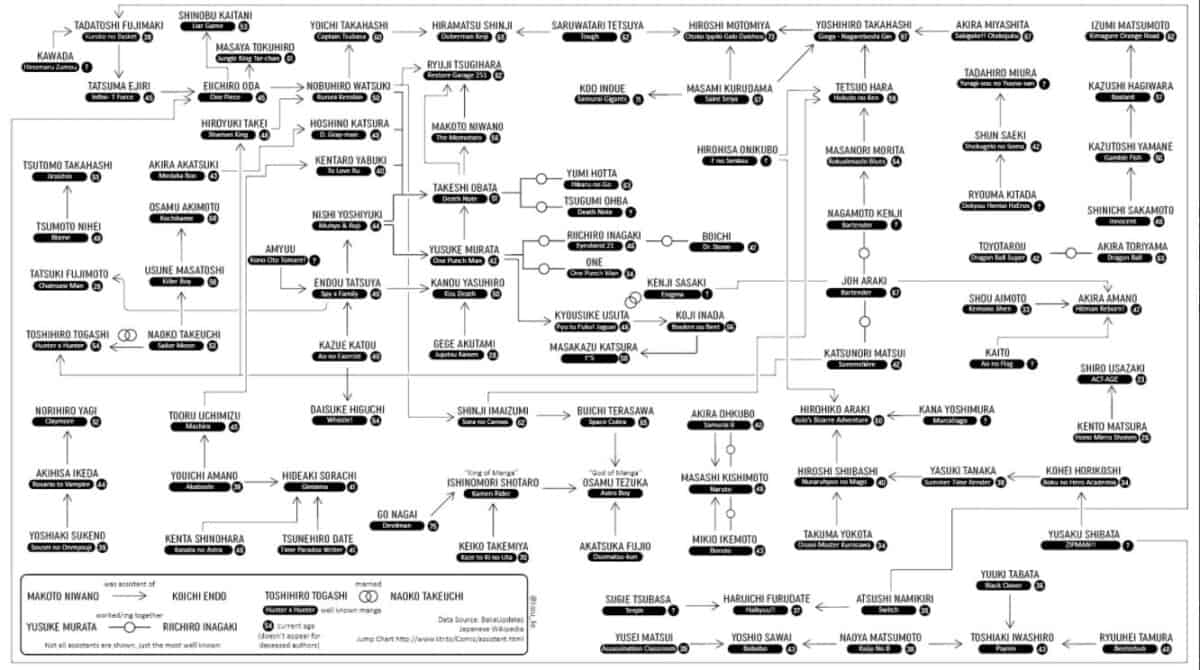
Mangakas don’t always share credit
You may want to know that some mangakas can be stingy in sharing credit. Mangaka assistants generally aren’t acknowledged in the releases on monthly manga magazines. However, they may be mentioned in the back of collected volumes.
Some artists claim that this is because assistants are just happy to contribute. This is the mindset of Eiichiro Oda, who doesn’t name his assistants even in tankobons. Still, there are mangakas like Hiro Mashima of Fairy Tail. He makes sure that his assistants are correctly identified and credited.
Now, it’s time to hear from you:
Did I miss anything?
Do you think that being a mangaka assistant is a good career choice?
Whatever your answer is, let’s hear it in the comments below.

